Volume 5 (2023)
Volume 4 (2022)
Volume 3 (2021)
Volume 2 (2020)
Volume 1 (2019)
Main Subjects = Analytical chemistry
Number of Articles: 65
Effect of vibration frequency on erythrocyte and platelets damage
Articles in Press, Accepted Manuscript, Available Online from 17 December 2023
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the impact of vibration frequency on the quality of blood components, specifically erythrocytes and Platelets. A device was developed to alter vibration ... Read MorePeripherally modified poly (acrylic acid)/ ZnO nanocomposite hydrogel with selective superadsorption properties
Volume 5, Issue 11 , November 2023, , Pages 1023-1037
Abstract
In this study, removal of three toxic chemical pollutants, such as crystal violet (CV) dye, tetracycline (TC) drug, and phenol (PH) using sodium alginate-g-poly (acrylicacid-co-sodium, ... Read MoreStructural design of biosensor: A review
Volume 5, Issue 10 , October 2023, , Pages 915-934
Abstract
The basic elements in biosensors are the recognition element, reporting element, and measuring device. The typical structure for the biosensing process to occur is the one where the ... Read MoreApplication of response surface methodology on efficiency of fig leaf activated carbon for removal of methylene blue dye
Volume 5, Issue 9 , September 2023, , Pages 794-811
Abstract
Fig leaves that have fallen off the tree are a common agricultural waste in Iraq. In this study, a very common used dye methylene blue (MB), was tested to be removed using a low-adsorbent ... Read MoreMicrowave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis as a nanocomposite with superior adsorption capacity for efficient removal of toxic Maxillon blue(GRL) dye from aqueous solutions
Volume 5, Issue 9 , September 2023, , Pages 832-841
Abstract
In this study, a microwave assisted hydrothermal technique was employed for the synthesis of CNT/ZnO nanocomposite. Carbon nanotubes were obtained from incineration stacks in furnaces. ... Read MoreSynthesis and characterization of some new heterocyclic compounds (hydroqinazoline and thiazinone) prepared from Schiff bases derived from flucytosine drug and study of biological activity
Volume 5, Issue 7 , July 2023, , Pages 642-660
Abstract
A series of some new heterocyclic six–membered compounds has been synthesized from Flucytosine drug, containing a terminal primary amine group, and was used to prepare a number ... Read MoreDetermination of manganese and selenium levels in Iranian herbal drops by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry technique
Volume 5, Issue 6 , June 2023, , Pages 569-575
Abstract
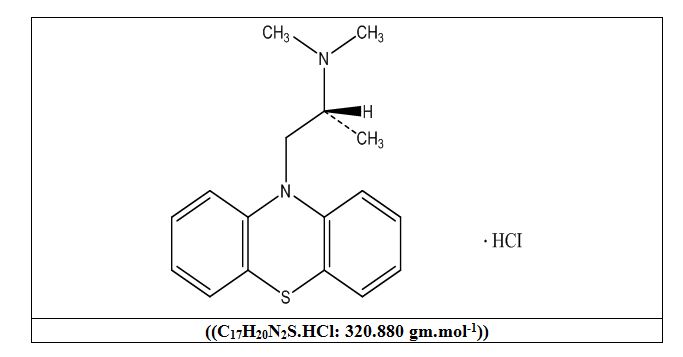
In the present work, Se and Mn analysis was carried out among some popular Iranian herbal drops to monitor a possible accumulation of adverse elements. In this study, five different ... Read MoreUltra violet estimation of promethazine HCl in pharmaceutical formulation and industrial waste water sample
Volume 5, Issue 5 , May 2023, , Pages 404-410
Abstract
A new method is proposed to detect and precisely determining of promethazine HCl. This procedure is easy, straightforward, quick, and cost-effective technique. It is applicable to a ... Read MoreSynthesis and characterization of new 4,6-dimethoxy-1H-indole derivatives as antibacterial and antitumor agents
Volume 5, Issue 5 , May 2023, , Pages 411-424
Abstract
New heterocyclic compounds derived from 4,6-Dimethoxy-1H-indole were synthesized. 4,6-Dimethoxy-1H-indole was reacted with chloroacetic acid to produce compound (R1) which used as starting ... Read MoreSynthesis, characterization, and studying of (thermal, spectral and physical) properties of new Schiff base monomers and liquid Crystal compounds from Ampicillin
Volume 5, Issue 3 , March 2023, , Pages 282-293
Abstract
This work presents syntheses of six new Schiff base compounds from Ampicillin, p-hydroxyl Benzaldehyde reacted with (pentanol, hexanol, and heptanol) to produce (4-pentloxy, 4- hexaloxy, ... Read MoreA new spectrophotometric method to estimate atenolol, amlodipine, and furosemide in pharmaceutical dosages
Volume 4, Issue 12 , December 2022, , Pages 1285-1294
Abstract
Atenolol, amlodipine, and furosemide are the most important medications that have been used to treat cardiovascular diseases. Due to this fact, we suggested a new method to estimate ... Read MoreInsecticide efficacy of medicines and chemicals during cats flea infestations in Tyumen
Volume 4, Issue 12 , December 2022, , Pages 1318-1323
Abstract
The study's main aim is to provide the results of therapeutic efficiency of Komfortis, Foresto and Fitoelita medical agents and chemicals used during flea infestation among domestic ... Read MoreDetermination of diosmin and quercetindihydrate through charge transfer interaction with 4-methylamino phenol and normal flow injection system with spectrophotometric detection
Volume 4, Issue 11 , November 2022, , Pages 1115-1129
Abstract
In this work, we used normal flow injection analysis for determining two drugs of Quercetindehydrate symbolized as QE and Diosmin symbolized as DSN. The aim was to develop a simple, ... Read MoreStudy of some chemical properties for imported frozen shrimp available in local markets
Volume 4, Issue 10 , October 2022, , Pages 930-937
Abstract
This research was conducted to study some chemical properties of frozen shrimp available in local markets, 24 samples were randomly collected for six imported commercial brands from ... Read MoreDetection of lead and cadmium in types of chips from local markets in Baghdad
Volume 4, Issue 10 , October 2022, , Pages 1026-1032
Abstract
Twenty-six samples of chips were examined by 13 chips samples as well as 13 samples of chips corn and all examined samples were analyzed by using the Flame Atomic Absorption Scale (AAS_7000( ... Read MoreSpectrophotometric determination of phenobarbital in pharmaceutical preparation using gold nanoparticles
Volume 4, Issue 9 , September 2022, , Pages 812-825
Abstract
A simple, rapid and accurate spectrophotometric method is proposed to determine Phenobarbital (PHB) based on the coupling of 2,6-Dichloroindophenol sodium salt hydrate (DSH) with PHB ... Read MoreSpectrophotometric determination of Mesalazine by formation of ion pair complex
Volume 4, Issue 9 , September 2022, , Pages 826-834
Abstract
A simple, developed, fast, and accurate spectrophotometric method was examined to determine Mesalazine (MES) in its pure form and pharmaceutical preparation (Pentasa). It was based ... Read MoreEstimation and development of some biophysical characteristics of the drug Favipiravir used in the treatment of corona-virus using green chemistry technology
Volume 4, Issue 9 , September 2022, , Pages 835-851
Abstract
This study included the preparation and identification of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuNPs) prepared from eucalyptus leaf extract using modern and advanced detection and analysis devices: ... Read MorePreparation and characterization of nano-carbon as an adsorbent for industrial water treatment
Volume 4, Issue 9 , September 2022, , Pages 852-862
Abstract
This study included the preparation and characterization of carbon nanoparticles prepared from environmentally friendly plant sources, namely a mixture of walnut shells and date kernels, ... Read MoreComparing the effect of drugs atorvastatin and rosuvastatin on the level of laboratory markers acute coronary syndrome patients
Volume 4, Issue 9 , September 2022, , Pages 894-899
Abstract
Pharmacotherapy is one of the most important measures for improving the health status of patients, which can play a key role in this regard. The present study was performed to compare ... Read MoreStudy of some physical changes of a binary combination of a drug Amphotericin B with Cetyl Trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB)
Volume 4, Issue 8 , August 2022, , Pages 741-749
Abstract
The research included studying the effectiveness of Amphotericin B with cactus aloe vera extract for its therapeutic properties by studying the physical changes with the surfactant ... Read MoreDetermination of catechol by continuous flow injection analysis via turbidmetric utilizing NAG-4SX3-3D analyzer
Volume 4, Issue 8 , August 2022, , Pages 790-805
Abstract
A simple and effective technique for detecting catechol by the generation of white precipitate utilizing the reaction of potassium dichromate with catechol in sulfuric acid medium, ... Read MoreLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopy as an unconventional tool analysis for carbon allotropes
Volume 4, Issue 8 , August 2022, , Pages 806-811
Abstract
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a new approach for determination and characterization of various nanomaterials structures. In this work, LIBS emission spectra of different ... Read MoreInvestigation of the π-bridge role for imidazole derivative dyes in dye sensitized solar cell: theoretical study
Volume 4, Issue 7 , July 2022, , Pages 598-606
Abstract
A series of metal-free imidazole derivative dyes (C2, C3, C4, and C5) are virtually designed based on the original synthesized dye (E)-3-(5-(4,5-bis(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)-1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)thiophen-2-yl)-2-cyanoacrylic ... Read MoreInvestigating the effect of methylprednisolone pulse on treatment of back pain
Volume 4, Issue 5 , May 2022, , Pages 366-371