Volume 5 (2023)
Volume 4 (2022)
Volume 3 (2021)
Volume 2 (2020)
Volume 1 (2019)
Main Subjects = Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Number of Articles: 21
The potential of 12 flavonoid compounds as alzheimer's inhibitors through an in silico approach
Articles in Press, Accepted Manuscript, Available Online from 10 November 2023
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disorders (NDD) are age-related condition characterized by a progressive decline in brain functions. This condition has influenced more than 8% of the adult population ... Read MoreThe antinociceptive effect of Chrysophyllum cainito L. leaves extract and tablet in wistar rats
Volume 5, Issue 12 , December 2023, , Pages 1055-1063
Abstract
Pain and inflammation in the joints from cartilage breakdown characterize osteoarthritis (OA), a degenerative disease linked to low estrogen levels. Because phytoestrogens can perform ... Read MoreCytotoxic activity of the purified extracts from duku (Lansium domesticum Corr.) Leaf against MCF-7 and HTB-183 cell lines, and the correlation with antioxidant activity
Volume 5, Issue 12 , December 2023, , Pages 1082-1095
Abstract
One of the plants that potential to develop as an anticancer agent is Duku leaf (Lansium domesticum Corr.). From previous studies, Duku leaf extract had cytotoxic activity against several ... Read MoreResveratrol in cancer chemotherapy: Is it a preventer, protector, or fighter?
Volume 5, Issue 7 , July 2023, , Pages 576-587
Abstract
Cancer is a virulent disease that is regarded as a black-hearted and evil-minded illness in many human civilizations because it develops silently and without warning until it reaches ... Read MoreA review of Schiff base-inorganic complexes and recent advances in their biomedicinal and catalytic attributes
Volume 5, Issue 6 , June 2023, , Pages 522-535
Abstract
Schiff base-inorganic complexes have significantly contributed to the development of modern drug design due to their significance in a number of multi-discipline study fields. This ... Read MoreSynthesis, in silico ADMET, docking, antioxidant, antibacterial and antifungal evaluations of some pyrimidine derivatives
Volume 5, Issue 3 , March 2023, , Pages 216-227
Abstract
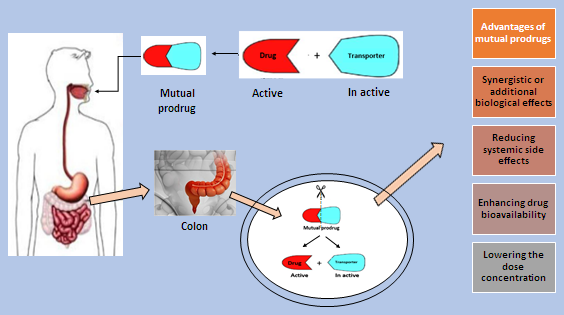
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile derivatives were synthesized (compounds 1a-d) by the Biginelli reaction of substituted aromatic aldehydes, cyano-ethyl acetate, and urea/thiourea ... Read MoreMutual prodrugs for colon targeting: A review
Volume 4, Issue 12 , December 2022, , Pages 1251-1265
Abstract
The goal of targeting drugs to a specific site or organ in the body is to achieve an ideal therapeutic effect with minimal harmful effects on the other components of the human body. ... Read MoreAntibacterial activity of Cassia angustifolia. Vahl (Sinameki) leaf extract against some pathogenic bacteria
Volume 4, Issue 11 , November 2022, , Pages 1108-1114
Abstract
Cassia angustifolia. Vahl (Sinameki) is one of the best-known medicinal herbs for the treatment of constipation in Iraq and many Arabic countries and it has long been used as a medicinal ... Read MoreSynthesis of disubstituted anisolodipyrone-derived ester compounds: The search for new bioactive candidates
Volume 4, Issue 11 , November 2022, , Pages 1171-1183
Abstract
In this study, ketone di-α-carboxylic acid prepared from the interaction between anhydrous citric acid and strong inorganic acid was included in the Pechmann-related condensation ... Read MoreChemical synthesis of various composites of chromen-2-one: A review
Volume 4, Issue 9 , September 2022, , Pages 877-893
Abstract
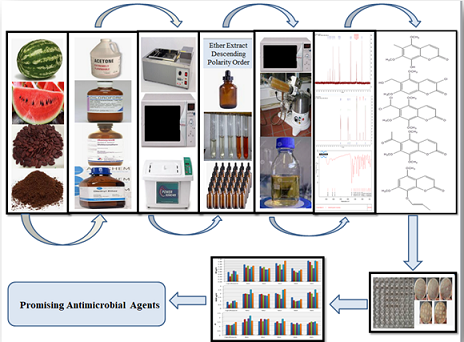
Chromen-2-one composites are a type of heterocycles that has a wide range of uses in healthcare technology, biological research, and a variety of commercial fields. Many attempts are ... Read MoreNovel coumarins isolated from the seeds of Citrullus lanatus as potential antimicrobial agents
Volume 4, Issue 8 , August 2022, , Pages 692-708
Abstract
In this study, four different solvents were utilized (acetone, chloroform, dichloromethane, and ether), with three extraction approaches as motion, ultrasonic bath-, and microwave oven-fostered ... Read MoreNovel naphthalene-derived coumarin composites: synthesis, antibacterial, and antifungal activity assessments
Volume 4, Issue 8 , August 2022, , Pages 709-724
Abstract
Composites with a coumarin-based chemical structure have sparked a lot of interest in the scientific community. This is because of their diverse structural properties and also, their ... Read MorePhytochemical, in vitro and in silico screening of roots of Jasminum auriculatum for antioxidant activity
Volume 4, Issue 8 , August 2022, , Pages 768-777
Abstract
Exploring the phytochemicals from traditional medicinal plants is essential for developing the novel leads for various diseases. In humans, many diseases are associated with the accumulation ... Read MoreNew fused-coumarin composites: synthesis, anticancer and antioxidant potentials evaluation
Volume 4, Issue 7 , July 2022, , Pages 607-619
Abstract
Today, there is a pressing need to develop anti-carcinogenic and anti-oxidative agents with the improved potency and fewer side effects. To this end, new coumarin composites were prepared ... Read MoreCancer-curative potential of novel coumarins from watermelon princess: A scenario of their isolation and activity
Volume 4, Issue 7 , July 2022, , Pages 657-672
Abstract
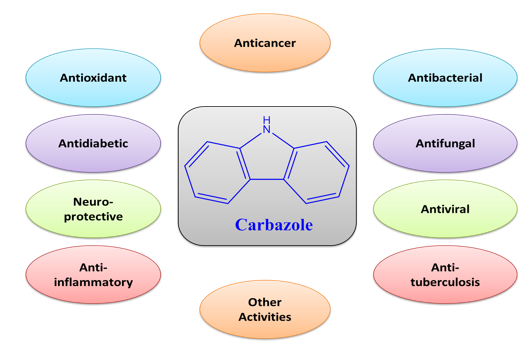
In this research, different types of solvents were used to isolate coumarins from the seeds of Watermelon Princess, including acetone, ether, chloroform, and dichloromethane. Isolation ... Read MoreA review on the biological potentials of carbazole and its derived products
Volume 4, Issue 6 , June 2022, , Pages 495-512
Abstract
Carbazoles are a type of heterocyclic compound which has been shown to have a variety of biological properties, including anti-tumor, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-epileptic, anti-diabetic, ... Read MoreExtraction and identification of the components of Thymbra spicata L. and Satureja khuzestanica Jamzad Oils native to Ilam province by headspace-solid phase microextraction (HS-SPME) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)
Volume 3, Issue 11 , November 2021, , Pages 841-853
Abstract
Satureja khuzistanica Jamzad (Lamiaceae) and Thymbra spicata L. (Lamiaceae) are medicinal plants belonging to the genera of Satureja and Thymbra, having many uses in traditional Iranian ... Read MoreRole of pyridazine analogs as acetylcholinesterase inhibitor: An approach for management of alzheimer’s disease
Volume 3, Issue 7 , July 2021, , Pages 435-442
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder causing failure of cognitive aptitude and performance irregularities, resulting in degradation of cerebral and psychological ... Read MoreProspects for the development of drugs with anti-viral activity based on licorice
Volume 3, Issue 5 , May 2021, , Pages 301-309
Abstract
The current situation with the widespread of a socially dangerous virus from the genus Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and the announcement of a pandemic in connection with this demand the ... Read MoreDevelopment of novel antibacterial gel using clove and calendula extracts with colloidal silver nanoparticles
Volume 3, Issue 3 , March 2021, , Pages 170-179
Abstract
This study focuses on obtaining an extract from clove and calendula plants with colloidal nanoparticles of silver in the presence of 40% propyleneglycol and preparation of hydrophilic ... Read MoreComparing different extraction methods for oral syrup formulation of major bioactive compounds from Cordia Myxa fruit
Volume 2, Issue 9 , September 2020, , Pages 953-960